What is a Structural Engineer?

A structural engineer is a professional who specializes in designing, analyzing, and ensuring the structural integrity and safety of buildings, bridges, dams, towers, and other structures. They apply engineering principles and mathematical calculations to determine the strength and stability of structures, ensuring that they can withstand the forces and loads they are subjected to.
How to Become a Structural Engineer?

To become a structural engineer, you typically need to follow these steps:
- Obtain a Bachelor’s Degree: Start by earning a bachelor’s degree in civil engineering or structural engineering from an accredited university or college. This program provides a strong foundation in mathematics, physics, structural analysis, materials science, and engineering principles.
- Gain Relevant Experience: While pursuing your degree, seek opportunities to gain practical experience in the field of structural engineering. This can be achieved through internships, cooperative education programs, or entry-level positions in engineering firms or construction companies. Practical experience allows you to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world projects and develop essential skills.
- Pursue Professional Licensure: To practice as a structural engineer, it is often necessary to obtain a professional license. Licensing requirements vary by country and state, but typically involve completing a certain number of years of relevant work experience under a licensed engineer, passing the Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) exam, and then completing the Principles and Practice of Engineering (PE) exam. These exams assess your knowledge and competence in engineering principles and ethics.
- Specialize in Structural Engineering: After obtaining a civil engineering degree, you may choose to specialize further in structural engineering. This can be done through graduate studies or postgraduate programs that offer specialization in structural engineering. Pursuing a master’s degree or Ph.D. in structural engineering can provide advanced knowledge and research opportunities in the field.
- Continual Professional Development: Structural engineering is a rapidly evolving field, and it is essential to stay updated with the latest industry standards, codes, and technological advancements. Engage in continuous learning through workshops, seminars, conferences, and professional development courses. This helps you stay current with best practices and enhances your skills and expertise.
- Join Professional Organizations: Consider joining professional organizations such as the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) or the Institution of Structural Engineers (IStructE). These organizations offer networking opportunities, resources, and access to industry publications. Engaging with professional communities can help you stay connected with the industry, collaborate with peers, and stay informed about industry trends.
- Gain Professional Experience: As you progress in your career, seek opportunities to gain diverse and challenging professional experiences. This can include working on a variety of projects, collaborating with architects and other engineering disciplines, and taking on increasing levels of responsibility. Building a strong professional portfolio and demonstrating your competence in handling complex projects can open doors to advancement and leadership positions.
- Consider Professional Certifications: In addition to licensure, you may choose to pursue professional certifications to further demonstrate your expertise and enhance your credibility. Organizations such as the Structural Engineering Certification Board (SECB) offer certifications like the Structural Engineering Certification and the Structural Engineering SE Licensure. These certifications require a combination of education, experience, and passing a rigorous examination.
Structural Engineer: Eligibility
The eligibility requirements to become a structural engineer may vary depending on the country and educational institutions. However, here are some general eligibility criteria to pursue a career in structural engineering:
- Educational Qualifications: Most structural engineering positions require a minimum of a bachelor’s degree in civil engineering or structural engineering from an accredited university or college. Some institutions may offer specific structural engineering programs at the undergraduate level.
- Mathematics and Science Background: A strong background in mathematics and science is essential for a career in structural engineering. Courses in calculus, algebra, geometry, physics, and mechanics are typically part of the curriculum. Proficiency in these subjects is necessary to understand and apply engineering principles.
- Entrance Exams: Some countries and educational institutions may require students to clear entrance exams for admission into engineering programs. These exams assess the aptitude and knowledge of applicants in subjects like mathematics, physics, and analytical reasoning.
Benefits of Becoming a Structural Engineer

Becoming a structural engineer offers numerous benefits, both professionally and personally. Here are some key advantages of pursuing a career in structural engineering:
- Exciting and Challenging Work: Structural engineers are involved in the design, analysis, and construction of various structures, including buildings, bridges, dams, and towers. This work offers intellectual challenges and opportunities to solve complex problems. Each project presents unique design requirements and constraints, making the field of structural engineering dynamic and stimulating.
- Contributing to Infrastructure Development: Structural engineers play a crucial role in shaping the built environment. By designing safe and efficient structures, they contribute to the development of infrastructure that enhances the quality of life for communities. This sense of contribution and the ability to create something tangible can be highly rewarding.
- Job Security and Demand: Structural engineers are in high demand globally due to the need for infrastructure development, urbanization, and maintenance of existing structures. The demand for skilled structural engineers remains consistently strong, providing job security and a wide range of career opportunities.
- Career Advancement Opportunities: Structural engineering offers a clear career progression path. As you gain experience and expertise, you can take on more challenging projects, assume leadership roles, and advance to positions such as project manager, senior engineer, or technical director. There are also opportunities to specialize in specific areas such as seismic design, high-rise structures, or sustainable design.
- Competitive Salary: The demand for structural engineers and their specialized skill set often translates into competitive salaries. With experience and expertise, structural engineers can earn attractive compensation packages.
- Collaborative Work Environment: Structural engineers often work in interdisciplinary teams that include architects, civil engineers, construction professionals, and other specialists. This collaborative work environment provides opportunities to learn from and interact with professionals from various fields, fostering professional growth and expanding your knowledge base.
- Continuous Learning and Skill Development: Structural engineering is a field that requires staying updated with evolving technologies, design codes, and construction practices. This continuous learning ensures that your skills remain relevant and allows you to keep up with industry advancements. There are ample opportunities for professional development through workshops, conferences, and training programs.
- International Opportunities: Structural engineering skills are transferable across borders, offering opportunities for work on international projects or in different countries. The global demand for infrastructure development creates prospects for working on diverse projects worldwide and gaining exposure to different design practices and cultural contexts.
- Prestige and Recognition: Structural engineers are highly respected professionals within the engineering community and the construction industry. Their expertise in ensuring the safety and stability of structures earns them recognition and esteem among their peers, clients, and stakeholders.
- Positive Impact on Society: Structural engineers make a significant impact on society by designing structures that are safe, sustainable, and resilient. Their work contributes to the well-being and safety of communities, protecting lives and property from structural failures and natural disasters.
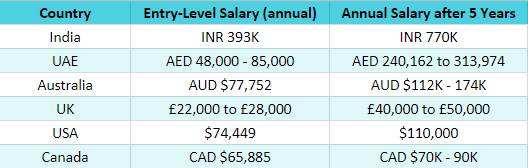
Jobs and Salary of Structural Engineer
| Job Title | Average Annual Salary (INR) |
| Graduate Structural Engineer | 3,00,000 – 6,00,000 |
| Junior Structural Engineer | 4,00,000 – 8,00,000 |
| Structural Engineer | 6,00,000 – 12,00,000 |
| Senior Structural Engineer | 10,00,000 – 20,00,000 |
| Principal Structural Engineer | 15,00,000 – 30,00,000 |
| Project Manager (Structural Engineering) | 12,00,000 – 25,00,000 |
Structural Engineer: FAQs
Q1: What does a structural engineer do?
A structural engineer is responsible for designing, analyzing, and ensuring the safety and integrity of structures such as buildings, bridges, dams, and towers. They use engineering principles and calculations to determine the strength and stability of structures, ensuring they can withstand various forces and loads.
Q2: What qualifications are required to become a structural engineer?
To become a structural engineer, you typically need a bachelor’s degree in civil engineering or structural engineering from an accredited institution. Some countries may also require professional licensure, which involves passing engineering exams and gaining relevant work experience.
Q3: What skills are important for a structural engineer?
Structural engineers require a combination of technical and soft skills. Technical skills include knowledge of structural analysis, design codes, and engineering software. Soft skills such as problem-solving, communication, attention to detail, and teamwork are also essential for effective project management and collaboration.
Q4: Is a master’s degree necessary to become a structural engineer?
While a master’s degree is not always required, it can enhance career prospects and provide advanced knowledge in structural engineering. Pursuing a master’s degree can be beneficial for those seeking specialization in a particular area or aiming for higher-level positions.
Q5: Can structural engineers work in different industries?
Yes, structural engineers can work in various industries, including construction, engineering consulting firms, government agencies, research institutions, and infrastructure development companies. They can also work on projects ranging from residential and commercial buildings to bridges, stadiums, and other large-scale structures.
Q6: How does structural engineering differ from civil engineering?
Structural engineering is a specialized discipline within civil engineering. While civil engineering encompasses multiple fields such as geotechnical engineering and transportation engineering, structural engineering specifically focuses on the design and analysis of structures to ensure their stability, strength, and safety.
Q7: What career opportunities are available for structural engineers?
Structural engineers can pursue various career paths, including roles such as structural design engineer, project engineer, senior engineer, project manager, and even entrepreneurship. They can work on diverse projects and specialize in areas such as seismic design, sustainable design, or specialty structures.
Q8: How is the job market for structural engineers?
The job market for structural engineers is generally favorable, with strong demand in industries related to construction, infrastructure development, and consulting. Factors such as urbanization, population growth, and infrastructure maintenance contribute to job opportunities for qualified structural engineers.
Q9: What professional organizations can structural engineers join?
Structural engineers can join professional organizations such as the Institution of Structural Engineers (IStructE), American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), and Structural Engineers Association (SEA) in their respective countries. These organizations provide networking opportunities, access to resources, and professional development activities.
Q10: Is continuing education necessary for structural engineers?
Yes, continuing education is important for structural engineers to stay updated with industry advancements, design codes, and emerging technologies. Participating in workshops, seminars, and conferences helps structural engineers enhance their skills, stay informed about industry trends, and maintain professional competence.
