Admission Requirements for US Universities
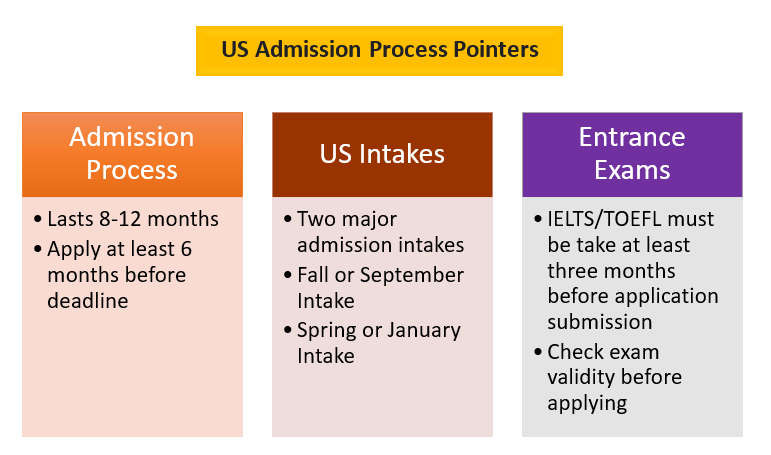
Admission requirements for US universities can vary significantly based on the type of institution (e.g., public or private), the level of degree (e.g., undergraduate or graduate), and the specific program of study. However, there are some common elements that most universities consider when evaluating applicants. Below, I’ll outline the general admission requirements for undergraduate and graduate programs in US universities:
Undergraduate Admission Requirements
- High School Diploma or Equivalent: Applicants must have completed their secondary education and obtained a high school diploma or an equivalent qualification recognized by the university.
- Academic Transcripts: Applicants are required to submit their official high school transcripts. These transcripts should include details of the courses taken and the grades received.
- Standardized Test Scores: Most US universities require standardized test scores as part of the application. The two most commonly accepted tests are the SAT (Scholastic Assessment Test) and the ACT (American College Testing). Some schools may also have specific requirements for SAT Subject Tests.
- English Language Proficiency: International applicants whose native language is not English are usually required to demonstrate English language proficiency through tests such as the TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language) or IELTS (International English Language Testing System).
- Letters of Recommendation: Many universities request letters of recommendation from teachers or counselors to assess an applicant’s academic abilities and personal qualities.
- Personal Statement or Essay: Applicants may be required to write a personal statement or essay, explaining their academic and career goals, as well as why they are interested in attending that particular university.
- Extracurricular Activities and Achievements: Universities often consider an applicant’s involvement in extracurricular activities, community service, and leadership roles.
- Application Fee: There is usually an application fee to submit the application for admission, though some universities offer fee waivers for students with financial need.
It’s important to note that admission requirements can vary from one university to another, and some highly competitive universities may have additional requirements.
Graduate Admission Requirements
Graduate programs in the US have more specialized admission requirements, and they vary depending on the field of study and the level of the degree (master’s or doctoral). Below are the typical requirements:
- Bachelor’s Degree: Applicants must hold a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution. The degree should be relevant to the field of study they are applying for.
- Academic Transcripts: Official transcripts of all previous academic coursework are required.
- Standardized Test Scores: Graduate Record Examination (GRE) scores are often required for many master’s and doctoral programs. Some programs may require subject-specific GRE scores or may accept other standardized tests like the GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test) for business programs.
- Letters of Recommendation: Applicants usually need to submit letters of recommendation from professors, employers, or other professionals who can speak to their academic abilities and potential for graduate study.
- Statement of Purpose: A statement of purpose or personal statement is required, detailing the applicant’s academic and career goals, research interests, and why they are interested in the specific graduate program.
- Resume/CV: A comprehensive resume or curriculum vitae (CV) highlighting academic achievements, work experience, research projects, publications, and relevant skills is often required.
- English Language Proficiency: Similar to undergraduate programs, international applicants need to demonstrate English language proficiency through tests like TOEFL or IELTS.
- Interviews or Portfolios: Some programs may require interviews, auditions, or submission of portfolios, especially for creative fields or performing arts programs.
- Application Fee: As with undergraduate applications, there is usually an application fee for graduate programs.
Course Structure for Studying in USA after 12th
Studying in the USA after completing 12th grade typically involves pursuing an undergraduate degree. The course structure may vary based on the specific university and program of study, but there are some general components that are common across most undergraduate programs.
Courses in USA after 12th: Key Highlight
| Field of Study | Course Name | Duration | Description |
| Business | Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) | 4 years | Focus on business principles, management, finance, marketing, accounting, and entrepreneurship. |
| Engineering | Bachelor of Science in Engineering | 4 years | Specializations in various engineering disciplines such as mechanical, electrical, civil, computer, etc. |
| Computer Science | Bachelor of Science in Computer Science | 4 years | Study of programming, algorithms, data structures, software development, and computer systems. |
| Medicine | Bachelor of Science in Nursing | 4 years | Preparation for a nursing career with courses in anatomy, physiology, patient care, and healthcare ethics. |
| Psychology | Bachelor of Arts in Psychology | 4 years | Study of human behavior, mental processes, psychological theories, and research methods. |
| Biology | Bachelor of Science in Biology | 4 years | Study of living organisms, genetics, ecology, physiology, and cellular biology. |
| Political Science | Bachelor of Arts in Political Science | 4 years | Exploration of political systems, international relations, public policy, and government institutions. |
| English Literature | Bachelor of Arts in English Literature | 4 years | Analysis of literature, critical thinking, literary theory, and language studies. |
| Fine Arts | Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) | 4 years | Specializations in painting, sculpture, photography, graphic design, and other visual arts. |
| Communication | Bachelor of Arts in Communication | 4 years | Study of media, journalism, public relations, digital communication, and interpersonal communication. |
Cost of Studying in USA after 12th

| Expense | Description |
| Tuition Fees | The cost of tuition varies widely based on the university and the program of study. This is the primary expense for education. |
| Room and Board | This includes the cost of accommodation (dormitory or off-campus housing) and meal plans. |
| Books and Supplies | The cost of textbooks, stationery, and other study materials. |
| Health Insurance | Many universities require international students to have health insurance coverage. |
| Personal Expenses | Daily living expenses, transportation, and other personal costs. |
| Application Fees | Non-refundable fees for applying to universities. |
| Visa Fees | Fees associated with obtaining a student visa to study in the USA. |
| Travel Expenses | Cost of travel to and from the USA and any travel within the country during breaks or holidays. |
| Miscellaneous Expenses | This includes costs for various campus services, club memberships, and other incidentals. |
Science and Engineering in USA after 12th

| Field of Study | Course Name | Degree Level | Duration | Description |
| Computer Science | Bachelor of Science in Computer Science | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Study of programming, algorithms, data structures, software development, computer systems, and artificial intelligence. |
| Mechanical Engineering | Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Focus on the design, analysis, and manufacturing of mechanical systems, machines, and devices. |
| Electrical Engineering | Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Study of electrical circuits, electronics, power systems, control systems, and telecommunications. |
| Civil Engineering | Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Concentration on the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure, buildings, and transportation systems. |
| Chemical Engineering | Bachelor of Science in Chemical Engineering | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Study of chemical processes, material synthesis, and the design of chemical plants and equipment. |
| Biomedical Engineering | Bachelor of Science in Biomedical Engineering | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Intersection of biology, medicine, and engineering to develop solutions for healthcare and medical devices. |
| Environmental Engineering | Bachelor of Science in Environmental Engineering | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Focus on environmental protection, sustainable practices, and the design of water and waste management systems. |
| Aerospace Engineering | Bachelor of Science in Aerospace Engineering | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Concentration on aircraft, spacecraft, and satellite design, propulsion systems, and aerodynamics. |
| Materials Science and Engineering | Bachelor of Science in Materials Science and Engineering | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Study of materials’ properties, structure, and behavior, with applications in various industries. |
| Bioengineering | Bachelor of Science in Bioengineering | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Integration of engineering principles with biological systems to develop medical and biotechnological solutions. |
Study Medical in USA after 12th
Studying medical in the USA after completing 12th grade typically involves pursuing a Bachelor of Science (BS) degree in a pre-medical or related field before applying to medical school. Below is a table outlining the general pathway to becoming a medical doctor in the USA after 12th grade.
| Step | Description |
| Step 1: Bachelor’s Degree | Pursue a 4-year Bachelor of Science (BS) degree in a pre-medical or related field. Common pre-med majors include Biology, Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Neuroscience. Students should focus on achieving a high GPA and taking pre-requisite courses like Biology, Chemistry, Physics, and Mathematics. |
| Step 2: MCAT | Take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT). The MCAT is a standardized test that assesses an applicant’s knowledge of scientific principles and critical thinking abilities. MCAT scores are a crucial factor in medical school admissions. |
| Step 3: Medical School | Apply to and attend a 4-year accredited medical school in the USA. Medical schools offer the Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree. During medical school, students undergo rigorous medical training, including clinical rotations in various specialties. |
| Step 4: Residency | After graduating from medical school, aspiring doctors must complete a residency program in their chosen medical specialty. Residencies typically last 3 to 7 years, depending on the specialty. During this period, residents receive supervised hands-on training in their chosen field. |
| Step 5: Fellowship (Optional) | Some medical specialties require additional training beyond residency, known as fellowships. Fellowships are optional but allow doctors to specialize further in specific areas of medicine. |
| Step 6: Licensure | Obtain a medical license to practice medicine independently. Licensure requirements vary by state and usually involve passing the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) or Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination (COMLEX). |
| Step 7: Board Certification (Optional) | Doctors can choose to become board-certified in their specialty by passing examinations administered by specialty-specific medical boards. Board certification demonstrates expertise and competence in the chosen medical field. |
Study Commerce in USA after 12th
| Name of the Course | Top Universities | Admission Deadlines |
| Bachelor of Accounting | University of Texas at Austin | Fall- December 1 Spring- October 1 |
| Bachelor of Management | University of Pennsylvania | January 1 |
| Bachelor of Finance | University of Pennsylvania | January 1 |
| Bachelor of Entrepreneurship | Babson College | January 2 |
| BSc in Economics | Harvard University | January 1 |
Study Arts in USA after 12th
Studying Arts in the USA after completing 12th grade typically involves pursuing a Bachelor of Arts (BA) degree in various disciplines. Below is a table outlining the general pathway for studying Arts in the USA after 12th grade, with some common arts disciplines and potential career paths.
| Arts Discipline | Course Name | Degree Level | Duration | Description | Potential Career Paths |
| English Literature | Bachelor of Arts in English Literature | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Analysis of literature, critical thinking, literary theory, and language studies. | Writer, Editor, Teacher, Communications Specialist |
| Fine Arts | Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Specializations in painting, sculpture, photography, graphic design, and other visual arts. | Visual Artist, Graphic Designer, Art Director, Illustrator |
| History | Bachelor of Arts in History | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Study of historical events, cultures, societies, and historical research methods. | Historian, Archivist, Museum Curator, Teacher |
| Psychology | Bachelor of Arts in Psychology | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Study of human behavior, mental processes, psychological theories, and research methods. | Psychologist (with further studies), Research Assistant |
| Sociology | Bachelor of Arts in Sociology | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Examination of human societies, social structures, and social behavior. | Social Worker, Research Analyst, Human Resources |
| Political Science | Bachelor of Arts in Political Science | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Exploration of political systems, international relations, public policy, and government institutions. | Politician, Public Policy Analyst, Government Relations |
| Anthropology | Bachelor of Arts in Anthropology | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Study of human cultures, societies, and human evolution. | Anthropologist, Archaeologist, Cultural Resource Manager |
| Theater and Drama | Bachelor of Arts in Theater | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Training in acting, stagecraft, theater history, and dramatic literature. | Actor, Director, Playwright, Drama Teacher |
| Communications | Bachelor of Arts in Communications | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Study of media, journalism, public relations, digital communication, and interpersonal communication. | Public Relations Specialist, Media Planner, Journalist |
| Music | Bachelor of Arts in Music | Bachelor’s | 4 years | Focus on music theory, performance, composition, and music history. | Musician, Music Teacher, Composer, Music Therapist |
Scholarships to Study in USA after 12th
| Scholarship Name | Description | Eligibility Criteria |
| Fulbright Foreign Student Program | Sponsored by the U.S. Department of State, the Fulbright program provides funding for graduate and postgraduate studies, including undergraduate degrees. | Open to students from eligible countries, with academic excellence and leadership potential. |
| Hubert Humphrey Fellowship Program | The Humphrey Fellowship program offers scholarships for professionals pursuing non-degree academic coursework and leadership development. | Open to students from eligible countries with a demonstrated commitment to public service. |
| Rotary Foundation Global Grants | Rotary Global Grants support international graduate students pursuing coursework or research abroad. | Applicants must have the sponsorship of a local Rotary club and meet academic and leadership criteria. |
| American University Emerging Global Leader Scholarship | This scholarship covers full tuition, room, and board for high-achieving international students who demonstrate leadership potential. | Open to first-year undergraduate students with strong academic records and leadership achievements. |
| Global UGRAD (Global Undergraduate Exchange Program) | Global UGRAD provides scholarships for one semester or academic year of undergraduate study at U.S. universities. | Open to students from select countries with excellent academic records and community involvement. |
| Joint Japan World Bank Graduate Scholarship Program | While mainly for graduate studies, this program also offers limited scholarships for undergraduate studies in specific fields. | Open to students from World Bank member countries pursuing studies in fields related to development. |
| International Students Academic Merit Scholarship | Offered by various universities, this scholarship provides financial assistance based on academic achievement. | Open to international students with excellent academic records applying to specific universities. |
| Merit-Based Scholarships | Many U.S. universities offer merit-based scholarships for exceptional international students. | Eligibility and application deadlines vary by university. |
FAQs
What are the admission requirements for studying in the USA?
Admission requirements vary depending on the level of study (undergraduate, graduate, or doctoral) and the institution you are applying to. Generally, you’ll need to submit academic transcripts, standardized test scores (such as SAT, ACT, GRE, or GMAT), letters of recommendation, a statement of purpose, and proof of English language proficiency (usually TOEFL or IELTS).
What is the academic year schedule in the USA?
The academic year typically starts in late August or early September and runs through May or June, divided into two semesters: fall and spring. Some institutions also offer a shorter summer session.
How do I obtain a student visa for the USA?
To obtain a student visa (F-1 visa), you must first be accepted by a SEVP-approved school in the USA. Then, you can apply for the F-1 visa at a U.S. embassy or consulate in your home country. You’ll need to provide relevant documents, including your Form I-20 (Certificate of Eligibility for Nonimmigrant Student Status), proof of financial support, and other required forms.
What are the major English language proficiency tests accepted by U.S. universities?
The most commonly accepted English language proficiency tests are TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language) and IELTS (International English Language Testing System). Some universities may also accept other tests like PTE (Pearson Test of English).
Are there scholarships available for international students in the USA?
Yes, there are scholarships and financial aid opportunities available for international students, though they may be limited. Many universities offer merit-based scholarships, and there are also private organizations and government-sponsored programs that provide financial support to international students.
How much does it cost to study in the USA?
The cost of studying in the USA can vary significantly depending on the institution, program, and location. Tuition fees for international students can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands of dollars per year. Additionally, you need to consider living expenses, such as accommodation, food, transportation, and health insurance.
Can international students work while studying in the USA?
Yes, international students on an F-1 visa are allowed to work on-campus for up to 20 hours per week during the academic year and full-time during scheduled breaks. However, off-campus work is generally restricted, and you would need to apply for specific work authorization.
What are the popular fields of study in the USA for international students?
The USA is renowned for offering a wide range of programs across various fields. Some popular choices for international students include Engineering, Computer Science, Business Administration, Health Sciences, Social Sciences, and Arts and Humanities.
Is health insurance mandatory for international students in the USA?
Yes, most universities in the USA require international students to have health insurance coverage during their studies. Some institutions provide their own health insurance plans, while others may allow students to purchase their own plans that meet specific requirements.
Can international students stay in the USA after completing their studies?
Yes, international students can apply for Optional Practical Training (OPT) after completing their degree, which allows them to work in the USA for up to one year. STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) students may be eligible for an extended 24-month OPT period. Some students may also explore other visa options like the H-1B visa for employment sponsorship.
