
Fashion Design

Fashion design is a creative and artistic process of conceiving and creating clothing, accessories, and footwear that are visually appealing, functional, and reflective of the designer’s unique vision and style. Fashion designers are individuals with a keen eye for aesthetics, a deep understanding of fabrics and materials, and a passion for innovation and self-expression. They play a significant role in shaping the fashion industry and influencing trends that define different eras and cultures.
Fashion Design: Key Highlight
| Aspect | Description |
| Definition | Creative and artistic process of conceiving and creating clothing, accessories, and footwear. |
| Inspirations | Drawn from art, nature, history, culture, and current events. |
| Sketching | Translating ideas into sketches for visualizing concepts. |
| Fabric Selection | Choosing appropriate fabrics for texture and aesthetics. |
| Pattern Making | Creating templates for garment construction. |
| Garment Construction | Assembling fabric pieces to create the desired silhouette. |
| Fittings and Iterations | Evaluating fit and making adjustments for better results. |
| Embellishments | Incorporating embroidery, beading, and other detailing. |
| Ready-to-Wear | Creating clothing for the mass market in standard sizes. |
| Haute Couture | Designing custom-made, high-end garments for individual clients. |
| Sustainable Fashion | Focusing on environmentally conscious and ethical practices. |
| Streetwear | Catering to urban and youth culture with edgy, casual style. |
| Bridal and Evening Wear | Specializing in exquisite gowns and dresses for occasions. |
| Impact | Influencing trends, culture, self-expression, and the global economy. |
Fashion Design: Eligibility
Eligibility criteria for pursuing a career in fashion design can vary depending on the educational institution and the level of study (e.g., undergraduate or postgraduate). However, in general, the following are the common eligibility requirements for aspiring fashion designers:
- Educational Qualifications:
- Undergraduate Programs: For a Bachelor’s degree in fashion design, candidates typically need to have completed their high school education or equivalent (e.g., A-levels, IB, etc.).
- Postgraduate Programs: To pursue a Master’s degree in fashion design, candidates must hold a Bachelor’s degree in fashion design or a related field.
- Portfolio: Many fashion design programs require applicants to submit a portfolio showcasing their artistic and creative abilities. The portfolio should include sketches, drawings, and examples of past design work that demonstrate the applicant’s talent and potential in fashion design.
- English Language Proficiency: For international students or in programs conducted in English, a minimum score in English language proficiency tests like IELTS or TOEFL might be required.
- Entrance Examinations: Some fashion design institutions conduct entrance exams or interviews to assess the aptitude and passion of candidates for fashion design.
- Personal Statement or Statement of Purpose: Applicants may be required to submit a written statement explaining their interest in fashion design and their career goals.
- Internship or Work Experience: Some institutions may consider work experience or internships in the fashion industry as an added advantage during the application process.
Fashion Design: Admission Process
The admission process for fashion design programs typically involves several steps that assess the candidate’s artistic abilities, creativity, and passion for the field. The process can vary depending on the educational institution and the level of study (e.g., undergraduate or postgraduate). Here is a general overview of the admission process for fashion design programs:
- Research and Selection of Institutes: Aspiring fashion designers should research different educational institutions that offer fashion design programs. They should consider factors such as the program’s curriculum, faculty expertise, facilities, reputation, and location. It is essential to choose institutes that align with the candidate’s interests and career goals.
- Application Form: Candidates need to fill out the application form provided by the institute of their choice. The form typically includes personal information, educational background, work experience (if any), and details about the program they wish to apply for.
- Portfolio Submission: One of the most critical aspects of the admission process is the portfolio submission. Candidates are required to prepare a portfolio showcasing their artistic skills, creativity, and design projects. The portfolio may include drawings, sketches, illustrations, photographs of garments, and any other relevant creative work.
- Entrance Examination/Interview: Many fashion design institutes conduct entrance examinations or interviews to assess the candidate’s aptitude, creativity, and passion for fashion design. The examination may include drawing tests, design challenges, or written components. Interviews provide an opportunity for candidates to discuss their design philosophy, inspirations, and career aspirations with the admissions committee.
- Statement of Purpose (SOP): Some institutes may require candidates to submit a written Statement of Purpose (SOP) or Personal Statement. In the SOP, candidates are expected to explain their interest in fashion design, their background, and why they wish to pursue the specific program.
- English Language Proficiency Test: For international students or programs conducted in English, candidates may be required to submit English language proficiency test scores, such as IELTS or TOEFL.
- Letters of Recommendation: Some institutes may request letters of recommendation from teachers, mentors, or employers who can attest to the candidate’s skills and potential in fashion design.
- Review and Selection: After completing the application process, the admissions committee reviews all the submitted materials, including the portfolio, entrance examination results, SOP, and recommendation letters. Candidates are then notified of the admission decision.
- Enrollment and Fees: If selected, candidates will receive an offer of admission, and they will need to complete the enrollment process, which may involve paying the required fees and providing additional documentation.
Fashion Design: Entrance Exams

| Entrance Exam | Conducting Body | Level of Study | Exam Format |
| NIFT Entrance Exam | National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) | Undergraduate & Postgraduate | CAT (Creative Ability Test) and GAT (General Ability Test) |
| NID Entrance Exam | National Institute of Design (NID) | Undergraduate & Postgraduate | DAT (Design Aptitude Test) and Portfolio Evaluation |
| AIEED Entrance Exam | ARCH College of Design & Business | Undergraduate & Postgraduate | GAT (General Ability Test) and Creative Aptitude Test |
| Pearl Academy Entrance Exam | Pearl Academy | Undergraduate & Postgraduate | Written Test, Personal Interview, and Portfolio Evaluation |
| UID Entrance Exam | Unitedworld Institute of Design (UID) | Undergraduate & Postgraduate | Design Aptitude Test (DAT) |
| Srishti Entrance Exam | Srishti Institute of Art, Design, and Technology | Undergraduate & Postgraduate | SEAT (Srishti Entrance and Aptitude Test) |
| CEED Entrance Exam | IIT Bombay | Postgraduate | Part A: Online Screening Test, Part B: Studio Test and Interview |
| FDDI Entrance Exam | Footwear Design and Development Institute (FDDI) | Undergraduate & Postgraduate | AIST (All India Selection Test) |
Fashion Design: Why Study?
Studying fashion design offers a wide range of opportunities and benefits that make it an appealing field for aspiring designers. Here are some compelling reasons to consider studying fashion design:
- Cultivate Creativity: Fashion design is a platform for artistic expression and creativity. Through studying fashion design, individuals can develop their artistic skills, experiment with various styles, fabrics, and techniques, and bring their unique visions to life through clothing and accessories.
- Learn the Craft: Fashion design programs provide comprehensive training in various aspects of the fashion industry. Students learn about garment construction, pattern making, draping, textiles, and fashion illustration, gaining a solid foundation in the technical aspects of the field.
- Explore Trend Forecasting: Fashion design programs often include courses on trend forecasting, enabling students to understand consumer behavior, market trends, and the evolving fashion landscape. This knowledge is essential for designing collections that resonate with consumers.
- Professional Development: Fashion design institutes offer a conducive environment for professional growth. Students receive guidance from experienced faculty, interact with industry professionals, and participate in internships, which can open doors to potential job opportunities.
- Embrace Innovation: Fashion is an ever-changing industry, and studying fashion design allows individuals to stay at the forefront of innovation. Students learn to incorporate new technologies, sustainable practices, and unconventional materials into their designs, contributing to the industry’s evolution.
- Business and Entrepreneurship Skills: Fashion design programs often include business-related courses, teaching students about marketing, brand management, and retail strategies. This knowledge equips aspiring designers with the skills to establish their own fashion brands or work in fashion management roles.
- International Exposure: Many fashion design institutes have collaborations with international universities or offer exchange programs. Studying fashion design in a diverse and global environment exposes students to different cultures, design philosophies, and industry practices.
- Networking Opportunities: Fashion design programs provide ample networking opportunities. Students interact with fellow designers, industry professionals, and potential employers, expanding their professional network and fostering collaborations.
- Pursue Personal Passions: Studying fashion design allows individuals to specialize in specific areas of interest, such as sustainable fashion, haute couture, sportswear, or accessories. This specialization enables them to pursue careers aligned with their passions.
- Contribution to Sustainability: Fashion design programs increasingly emphasize sustainability and ethical practices. Students learn about eco-friendly materials, responsible production processes, and circular fashion, contributing to a more sustainable future for the fashion industry.
- Impact on Society: Fashion has a profound influence on culture, society, and individual identity. As a fashion designer, one can contribute to social change, challenge norms, and promote diversity and inclusivity through their designs.
Fashion Design: Job and Salary
| Job Role | Average Salary (INR per annum) |
| Fashion Designer | 3,00,000 – 8,00,000 |
| Textile Designer | 2,50,000 – 6,00,000 |
| Fashion Illustrator | 2,00,000 – 5,00,000 |
| Fashion Stylist | 2,00,000 – 6,00,000 |
| Fashion Merchandiser | 3,00,000 – 7,00,000 |
| Pattern Maker | 2,00,000 – 5,00,000 |
| Apparel Production Manager | 4,00,000 – 10,00,000 |
| Fashion Coordinator | 2,50,000 – 6,00,000 |
| Fashion Blogger/Influencer | Earnings vary (from sponsorships, partnerships, etc.) |
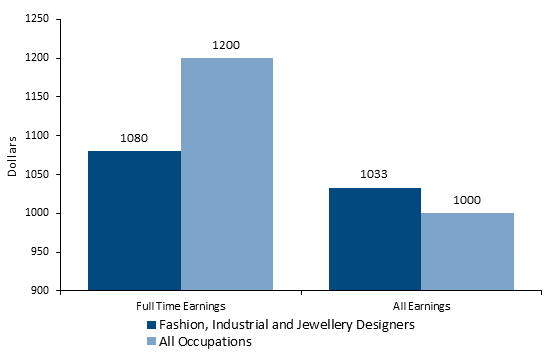
Post Graduate Diploma in Fashion Designing: Recommended Books
Some of the important reference books are mentioned below:
| Name of the Books | Authors |
| Patternmaking for fashion design fifth edition | Helen Joseph Armstrong |
| Fashion flats and Technical drawing | Bina Abling and Felice Docosta |
| The ancient world | Alex woolf |
| Complete book of curtains, Drapes and blinds | Wendy Baker |
| Painting, stamping, stenciling and embossing fabric | sandy Scrivano |
Fashion Design: Future Scope
Fashion design offers a promising and dynamic future with numerous opportunities for growth and innovation. The field continues to evolve, adapting to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and global trends. Here are some key aspects of the future scope in fashion design:
- Sustainability and Ethical Fashion: With a growing awareness of environmental issues, there is an increasing demand for sustainable and ethically produced fashion. Fashion designers who incorporate eco-friendly materials, adopt ethical practices, and embrace circular fashion concepts will be in high demand.
- Technology Integration: Technology is transforming the fashion industry, with advancements in 3D printing, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence. Fashion designers who are well-versed in these technologies will have a competitive edge in creating innovative designs and streamlining production processes.
- Personalization and Customization: Consumers are seeking unique and personalized fashion experiences. Fashion designers who can offer customizable and made-to-order designs will cater to this demand, creating a niche market for bespoke fashion.
- E-commerce and Digital Platforms: The rise of e-commerce and digital platforms has opened up new avenues for fashion designers to reach a global audience. Those who embrace online retail and digital marketing strategies will have access to a broader customer base.
- Sustainable Fashion Start-ups: The fashion industry is witnessing a rise in sustainable fashion start-ups that focus on ethical practices, transparency, and social impact. Fashion designers with innovative ideas can collaborate with such start-ups or launch their own sustainable fashion brands.
- Cross-Cultural Influences: As fashion becomes increasingly globalized, designers who draw inspiration from diverse cultures and blend different design elements will create unique and inclusive fashion collections.
- Fashion Technology and Wearable Tech: The fusion of fashion and technology has given rise to wearable tech, smart textiles, and functional fashion. Fashion designers who can combine aesthetics with technology will lead in this emerging field.
- Collaboration with Other Industries: Fashion designers are increasingly collaborating with other industries such as art, technology, and architecture to create cross-disciplinary designs and products.
- Niche Markets: There is a growing demand for niche fashion markets, such as sustainable activewear, modest fashion, plus-size fashion, and gender-inclusive designs. Fashion designers who cater to these specific markets can find significant opportunities for growth.
- Fashion Education and Research: As the fashion industry evolves, the need for skilled professionals and researchers in fashion design will increase. Opportunities in academia and research institutes can be pursued by experienced designers.
Fashion Design: FAQs
Q1: What is fashion design?
A1: Fashion design is a creative and artistic process of conceiving and creating clothing, accessories, and footwear that are visually appealing, functional, and reflective of the designer’s unique vision and style.
Q2: What skills are required to become a successful fashion designer?
A2: To become a successful fashion designer, one needs a combination of artistic skills, creativity, knowledge of fabrics and textiles, proficiency in pattern making, garment construction, and sewing, as well as an understanding of the fashion industry, market trends, and consumer preferences. Strong communication, problem-solving, and business skills are also essential.
Q3: What are the educational requirements for pursuing a career in fashion design?
A3: Educational requirements for fashion design vary, but most aspiring designers pursue a Bachelor’s degree in Fashion Design or a related field. Some may also opt for Master’s programs to further specialize in specific areas of fashion design.
Q4: What is a fashion design portfolio, and why is it important?
A4: A fashion design portfolio is a collection of an individual’s best design work, including sketches, illustrations, photographs of garments, and other creative projects. It is crucial for aspiring designers as it showcases their talent, creativity, and design skills to potential employers or fashion design institutes during the admission or hiring process.
Q5: What career opportunities are available in fashion design?
A5: Fashion design offers a wide range of career opportunities, including working as a fashion designer for a fashion house or a brand, textile designer, fashion illustrator, fashion stylist, fashion merchandiser, pattern maker, apparel production manager, and more. Some designers also choose to establish their own fashion brands or work as freelance designers.
Q6: What are some emerging trends in the fashion design industry?
A6: Some emerging trends in the fashion design industry include a focus on sustainable and ethical fashion, the integration of technology such as 3D printing and wearable tech, customization and personalization, and the rise of niche markets like sustainable activewear and gender-inclusive designs.
Q7: How does fashion design impact society and culture?
A7: Fashion design plays a significant role in shaping society and culture. It influences how people dress, express their identity, and participate in cultural trends. Fashion also reflects social values and can be a form of artistic expression that represents various cultural narratives and historical periods.
Q8: Is fashion design a competitive field?
A8: Yes, fashion design is a highly competitive field. The industry attracts a large number of talented and creative individuals. To succeed, aspiring fashion designers need to continuously develop their skills, stay updated on industry trends, and find ways to differentiate themselves and their designs.
Q9: Can I pursue a career in fashion design without a formal education?
A9: While a formal education in fashion design can provide valuable skills, it is possible to pursue a career in fashion design without a degree. Some successful designers are self-taught or have learned through practical experience and internships. A strong portfolio and a passion for fashion are essential in such cases.
Q10: How can I stay relevant and competitive in the fashion design industry?
A10: To stay relevant and competitive in the fashion design industry, designers should continuously seek inspiration, stay updated on fashion trends, improve their technical skills, embrace sustainability and technology, network with industry professionals, and be open to learning and adapting to the evolving demands of the market.