Best Engineering Courses for Future
In the ever-evolving world of technology and innovation, engineering plays a crucial role in shaping the future. Several engineering courses stand out as essential for meeting the demands of the future. Computer Science and Engineering is a dynamic field that focuses on software development, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity, catering to the rapidly expanding digital landscape.
Biomedical Engineering addresses the healthcare challenges of tomorrow, integrating engineering principles with medical sciences to design advanced medical devices and technologies. Renewable Energy Engineering is pivotal in the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, harnessing the power of clean resources like solar and wind.
Robotics and Automation Engineering is at the forefront of industrial advancements, creating intelligent machines that enhance productivity and efficiency. Lastly, Environmental Engineering emphasizes ecological preservation, offering innovative solutions to combat environmental issues and promote a greener world. These engineering courses not only open doors to exciting career opportunities but also empower individuals to contribute significantly to a brighter and more sustainable future.
List of Best Engineering Courses for Future

- Computer Science and Engineering
- Biomedical Engineering
- Renewable Energy Engineering
- Robotics and Automation Engineering
- Environmental Engineering
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Engineering
- Aerospace Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Chemical Engineering
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering
- Data Science and Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Materials Science and Engineering
- Mechatronics Engineering
- Nuclear Engineering
- Petroleum Engineering
- Software Engineering
- Structural Engineering
- Telecommunications Engineering
- Transportation Engineering
20 Best Engineering Jobs for the Future
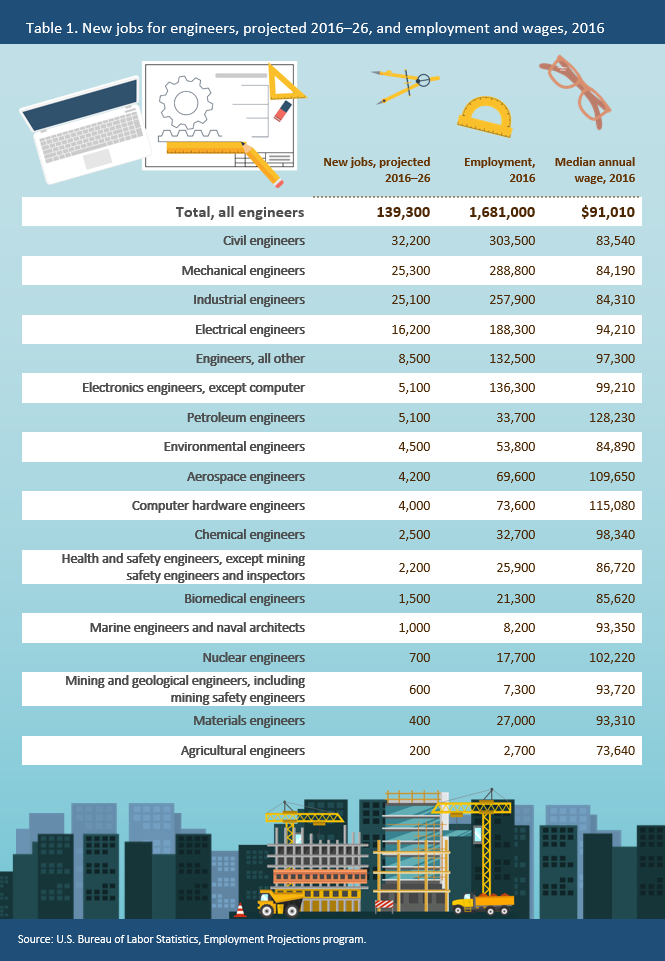
- Artificial Intelligence Engineer
- Data Scientist
- Robotics Engineer
- Cybersecurity Engineer
- Renewable Energy Engineer
- Biomedical Engineer
- Aerospace Engineer
- Environmental Engineer
- Civil Engineer (with a focus on sustainable infrastructure)
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Automation Engineer
- Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality (AR/VR) Engineer
- Blockchain Engineer
- Internet of Things (IoT) Engineer
- Autonomous Vehicle Engineer
- Energy Storage Engineer
- 3D Printing Engineer
- Smart Grid Engineer
- Urban Planner (with a focus on sustainable city development)
- Space Engineer
Average Salary in India
| Engineering Job | Average Salary Range (INR) |
| Artificial Intelligence Engineer | 8,00,000 – 20,00,000 |
| Data Scientist | 6,00,000 – 18,00,000 |
| Robotics Engineer | 6,00,000 – 15,00,000 |
| Cybersecurity Engineer | 6,00,000 – 18,00,000 |
| Renewable Energy Engineer | 4,50,000 – 12,00,000 |
| Biomedical Engineer | 4,00,000 – 10,00,000 |
| Aerospace Engineer | 5,00,000 – 15,00,000 |
| Environmental Engineer | 4,00,000 – 12,00,000 |
| Civil Engineer (Sustainable Infrastructure) | 4,00,000 – 10,00,000 |
| Machine Learning Engineer | 6,00,000 – 18,00,000 |
| Automation Engineer | 4,00,000 – 10,00,000 |
| AR/VR Engineer | 4,50,000 – 12,00,000 |
| Blockchain Engineer | 6,00,000 – 15,00,000 |
| IoT Engineer | 4,50,000 – 12,00,000 |
| Autonomous Vehicle Engineer | 6,00,000 – 15,00,000 |
| Energy Storage Engineer | 4,50,000 – 12,00,000 |
| 3D Printing Engineer | 4,50,000 – 10,00,000 |
| Smart Grid Engineer | 4,50,000 – 12,00,000 |
| Urban Planner (Sustainable Development) | 4,00,000 – 10,00,000 |
| Space Engineer | 5,00,000 – 15,00,000 |
Most Demanding Engineering Field in Future 2025

In the future, the engineering fields that are expected to be in high demand by 2025 include:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Engineering
- Data Science and Analytics
- Cybersecurity Engineering
- Renewable Energy Engineering
- Biomedical Engineering
- Robotics and Automation Engineering
- Environmental Engineering
- Aerospace Engineering
- Civil Engineering (with a focus on sustainable infrastructure)
- Software Engineering (especially in emerging technologies)
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is a rapidly growing field that involves manipulating and controlling matter at the nanoscale level, typically within the range of 1 to 100 nanometers. It encompasses various disciplines such as physics, chemistry, materials science, and engineering. Nanotechnology has significant potential to revolutionize multiple industries and create groundbreaking innovations.
Petroleum Engineering
Petroleum Engineering is a specialized field of engineering that focuses on the exploration, extraction, production, and management of oil and gas resources. Petroleum engineers play a crucial role in the energy industry, contributing to the efficient and sustainable extraction of hydrocarbons from underground reservoirs.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that focuses on the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to learn and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. It involves the study of statistical models and algorithms that allow machines to automatically analyze and interpret complex patterns and data, and improve their performance over time through experience.
Machine Learning has significant implications and future prospects across various industries and domains.
Biomedical Engineering
Biomedical Engineering is a multidisciplinary field that combines principles of engineering, biology, and medicine to develop innovative solutions for healthcare and improve the quality of patient care. It involves the application of engineering principles and techniques to design, develop, and evaluate medical devices, diagnostic tools, therapeutic systems, and healthcare technologies.
Telecommunication Engineering
Telecommunication Engineering is a branch of engineering that focuses on designing, implementing, and managing communication systems and networks. It involves the transmission of information, such as voice, data, and video, over various communication channels, including wired and wireless technologies.
Required Skills for Engineering Students
| Skill Category | Skills |
| Technical Skills | – Mathematics and Advanced Calculus |
| – Physics and Applied Sciences | |
| – Computer Programming and Coding | |
| – Engineering Software and Tools | |
| – Technical Drawing and CAD (Computer-Aided Design) | |
| – Circuit Design and Electronics | |
| – Materials Science and Engineering | |
| – Data Analysis and Interpretation | |
| – Problem-solving and Troubleshooting Skills | |
| Communication | – Written and Verbal Communication |
| – Technical Report Writing | |
| – Presentation Skills | |
| – Active Listening | |
| – Collaboration and Teamwork | |
| – Interpersonal Skills | |
| – Cross-cultural Communication | |
| – Client and Stakeholder Engagement | |
| – Negotiation and Persuasion Skills | |
| – Technical Documentation | |
| – Project Management | |
| Analytical Skills | – Critical Thinking and Analytical Reasoning |
| – Problem-solving and Decision-making | |
| – Research and Information Gathering | |
| – Data Analysis and Interpretation | |
| – Statistical Analysis | |
| – Experimental Design and Analysis | |
| – Attention to Detail and Precision | |
| – Ability to Learn and Apply New Technologies | |
| Personal Skills | – Time Management and Organization |
| – Adaptability and Flexibility | |
| – Initiative and Self-motivation | |
| – Creativity and Innovation | |
| – Professional Ethics and Integrity | |
| – Leadership and Management Skills | |
| – Stress Management and Resilience | |
| – Continuous Learning and Professional Development | |
| – Problem-solving and Troubleshooting Skills |
Popular Certification and Professional Courses After Engineering
| Certification/Professional Course | Description |
| Project Management Professional (PMP) | A globally recognized certification for project management. |
| Six Sigma Green Belt/Black Belt | Certifications in process improvement and quality control. |
| Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) | Certification in networking and Cisco technologies. |
| AWS Certified Solutions Architect | Certification in Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud computing. |
| Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate | Certification in Microsoft Azure cloud platform. |
| Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) | Certification in cybersecurity and information security management. |
| Certified Data Scientist (CDS) | Certification validating skills in data science and analytics. |
| Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) | Certification in Scrum methodology for agile project management. |
| Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) | Certification in ethical hacking and penetration testing. |
| Autodesk Certified Professional (ACP) | Certification in computer-aided design (CAD) software. |
| Certified Energy Manager (CEM) | Certification in energy management and conservation. |
| Lean Six Sigma Certification | Certification in Lean Six Sigma methodologies for process improvement. |
| Certified Professional in Healthcare Quality (CPHQ) | Certification for quality improvement in healthcare systems. |
| Google Analytics Individual Qualification (GAIQ) | Certification in web analytics and data analysis with Google Analytics. |
| Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) | Professional qualification for investment and financial analysis. |
| Project Management Institute Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP) | Certification in Agile project management. |
| Certified SolidWorks Professional (CSWP) | Certification in 3D modeling using SolidWorks software. |
| Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) | Certification in information systems auditing and control. |
| Certified Reliability Engineer (CRE) | Certification for reliability engineering and maintenance optimization. |
| Certified Professional in Engineering Management (CPEM) | Certification in engineering management and leadership. |
| Certified Big Data Professional (CBDP) | Certification in big data technologies and analytics. |
Eligibility Criteria For Best Engineering Course
Eligibility criteria for the best engineering courses typically include:
- Academic Qualifications: Completion of high school education or equivalent with a strong background in science and mathematics.
- Entrance Exams: Clearing national or state-level engineering entrance exams, such as JEE Main, JEE Advanced, or other relevant exams specific to the country or region.
- Minimum Marks: Meeting the minimum required marks or percentage in the qualifying exams or entrance tests.
- Subject Requirements: Having studied specific subjects like Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics in the qualifying exams.
- Age Limit: Some courses may have specific age limits for eligibility.
- Residency/Citizenship: For certain courses, candidates may need to be citizens or residents of the country where the course is offered.
Global Universities for Pursuing Best Engineering Courses in the Future
| University | Country | Annual Fees (Approx.) | Website |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) | United States | $53,450 | www.mit.edu |
| Stanford University | United States | $55,473 | www.stanford.edu |
| California Institute of Technology (Caltech) | United States | $56,862 | www.caltech.edu |
| University of Cambridge | United Kingdom | £9,250 (EU/UK), £30,000 (Non-EU/UK) | www.cam.ac.uk |
| University of Oxford | United Kingdom | £9,250 (EU/UK), £30,000 (Non-EU/UK) | www.ox.ac.uk |
| ETH Zurich – Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich | Switzerland | CHF 1,320 (EU/EEA), CHF 1,600 (Non-EU/EEA) | www.ethz.ch |
| National University of Singapore (NUS) | Singapore | SGD 29,050 | www.nus.edu.sg |
| Tsinghua University | China | CNY 55,000 (Undergraduate), CNY 70,000 (Graduate) | www.tsinghua.edu.cn |
| University of Tokyo | Japan | ¥585,800 (Undergraduate), ¥535,800 (Graduate) | www.u-tokyo.ac.jp |
| Delft University of Technology | Netherlands | €2,168 (EU/EEA), €18,500 (Non-EU/EEA) | www.tudelft.nl |
Career Scope In Engineering Course
Engineering offers a wide range of career opportunities across various industries and sectors. Here are some of the career scopes in engineering:
- Aerospace Engineering: Careers in aerospace engineering involve designing, manufacturing, and testing aircraft, spacecraft, and related systems. Professionals in this field can work for aerospace companies, research institutions, and government agencies.
- Civil Engineering: Civil engineers are involved in the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure projects such as buildings, roads, bridges, and water supply systems. They can work in construction firms, government organizations, or as consultants.
- Mechanical Engineering: Mechanical engineers work on the design, development, and operation of mechanical systems and equipment. They find employment in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, energy, and robotics.
- Electrical Engineering: Electrical engineers specialize in the study and application of electrical systems, including power generation, electronics, and telecommunications. They can work in industries such as energy, telecommunications, electronics, and automation.
- Chemical Engineering: Chemical engineers work with chemicals, materials, and processes to design and optimize chemical reactions and production processes. They find opportunities in industries such as pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, food processing, and environmental engineering.
- Computer Science and Engineering: This field involves the development of computer software, hardware, and networks. Professionals in computer science and engineering can work in software development companies, IT consulting firms, research organizations, and technology companies.
- Environmental Engineering: Environmental engineers focus on designing and implementing solutions for environmental protection and sustainable development. They can work in areas such as water and wastewater treatment, waste management, and environmental consultancy.
Top Recruiters for Engineering Students
| Company | Industry |
| Technology | |
| Microsoft | Technology |
| Apple | Technology |
| Amazon | E-commerce/Technology |
| Tesla | Automotive/Energy |
| General Electric (GE) | Manufacturing/Energy |
| IBM | Technology/Consulting |
| Boeing | Aerospace/Defense |
| Intel | Semiconductors/Technology |
| Siemens | Engineering/Technology |
| ExxonMobil | Oil and Gas |
| General Motors (GM) | Automotive |
| Ford Motor Company | Automotive |
| Samsung | Technology/Electronics |
| Qualcomm | Semiconductors/Technology |
| Lockheed Martin | Aerospace/Defense |
| Infosys | Information Technology/Consulting |
| Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) | Information Technology/Consulting |
| Accenture | Consulting/Technology |
| Deloitte | Consulting/Professional Services |
| Shell | Oil and Gas |
| Schlumberger | Oilfield Services |
| Cisco Systems | Networking/Technology |
| Social Media/Technology | |
| Oracle | Technology/Database Management |
FAQs
Q: What are the popular engineering courses?
A: Some popular engineering courses include Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Engineering, Aerospace Engineering, Chemical Engineering, and Biomedical Engineering, among others.
Q: What is the duration of an engineering course?
A: The duration of an undergraduate engineering course is typically four years. However, the duration may vary depending on the country and specific program. Postgraduate engineering courses can range from one to two years or more, depending on the level of study.
Q: What are the job prospects for engineering graduates?
A: Engineering graduates have diverse job prospects in various industries such as manufacturing, construction, automotive, aerospace, technology, healthcare, energy, and consulting. They can work as engineers, researchers, consultants, project managers, analysts, and technical specialists, among other roles.
Q: What skills are essential for a successful engineering career?
A: Essential skills for a successful engineering career include technical knowledge in the chosen field, problem-solving and analytical skills, creativity and innovation, communication and teamwork, adaptability, and continuous learning. Strong mathematical and computational skills are also valuable.
Q: What is the average salary for engineering jobs?
A: The average salary for engineering jobs varies depending on factors such as the engineering field, level of experience, location, and industry. Salaries can range from moderate to high, with experienced professionals often earning higher incomes. It’s important to research specific engineering disciplines and industries to get a more accurate understanding of salary ranges.
Q: Are there opportunities for specialization within engineering fields?
A: Yes, engineering fields offer various opportunities for specialization. For example, within Mechanical Engineering, one can specialize in areas such as robotics, automotive engineering, or HVAC systems. Similarly, within Computer Science and Engineering, specializations can include artificial intelligence, data science, or software engineering. Specializations allow engineers to develop expertise in specific areas of interest.
Q: Is it necessary to pursue higher education or a master’s degree after completing an undergraduate engineering course?
A: Pursuing higher education or a master’s degree after completing an undergraduate engineering course is a personal choice. While some professionals opt for higher studies to specialize further or enhance career prospects, others directly enter the job market. The decision depends on individual career goals, industry requirements, and personal preferences.
Q: Are there opportunities for research and development (R&D) in engineering?
A: Yes, engineering offers significant opportunities for research and development. Many industries, universities, and research institutions conduct R&D activities to innovate, improve existing technologies, and develop new solutions. Engineers with research-oriented interests can pursue careers in R&D departments, research labs, or academic institutions.
Q: Can engineering graduates work in non-engineering roles?
A: Yes, engineering graduates possess a versatile skill set that is valued beyond traditional engineering roles. They can work in non-engineering roles such as management, consulting, finance, business development, technical sales, and entrepreneurship. The problem-solving and analytical abilities acquired during engineering studies are transferable to various industries and sectors.
Q: How can I stay updated with the latest advancements in the engineering field?
A: Staying updated with the latest advancements in the engineering field is essential. You can do so by regularly reading engineering journals, subscribing to industry newsletters, attending conferences and seminars, joining professional engineering associations, participating in online courses and webinars, and engaging in continuous learning and professional development activities.
