What is Aerospace Engineer?
An aerospace engineer is a professional who specializes in designing, developing, and maintaining various types of aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and related systems. Aerospace engineering is a branch of engineering that encompasses the design, construction, testing, and operation of vehicles and systems that navigate through the Earth’s atmosphere and outer space.
Aerospace engineers are involved in every stage of the aerospace product lifecycle, from conceptual design and analysis to manufacturing, testing, and maintenance. Their work is focused on ensuring the safety, efficiency, and reliability of aerospace systems.
How to become Aerospace Engineer?

To become an aerospace engineer, you typically need to follow these steps:
- Obtain a Bachelor’s Degree: Start by earning a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a related field, such as mechanical engineering with a focus on aerospace. Look for accredited programs that provide a comprehensive curriculum covering the fundamentals of aerospace engineering, including aerodynamics, flight mechanics, propulsion systems, and materials science.
- Gain Relevant Skills and Knowledge: During your undergraduate studies, focus on building a strong foundation in mathematics, physics, and computer science. Take advantage of opportunities to gain practical experience through internships, research projects, or participation in aerospace-related clubs or competitions. This will help you develop technical skills and a deeper understanding of aerospace engineering principles.
- Pursue Advanced Education (Optional): While not always required, obtaining a master’s or doctoral degree in aerospace engineering can enhance your knowledge and career prospects, especially if you plan to work on advanced research or specialized areas within the field. Advanced degrees can also open doors to leadership positions or teaching and research roles.
- Gain Work Experience: Seek internships or co-op positions with aerospace companies or research institutions to gain hands-on experience in the field. This practical experience will complement your academic studies and help you develop a better understanding of the industry. Consider joining professional organizations such as the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) to network with professionals and stay updated on industry developments.
- Obtain Professional Licensure (Optional): While licensure is not typically required for entry-level positions in aerospace engineering, becoming a licensed Professional Engineer (PE) can enhance your professional credibility and career advancement opportunities. Requirements for licensure vary by country or state, but generally involve completing an accredited engineering program, gaining relevant work experience, and passing a licensure exam.
- Stay Updated and Continuously Learn: Aerospace engineering is a dynamic field that evolves rapidly. Stay abreast of the latest advancements, industry trends, and emerging technologies. Engage in professional development activities such as attending conferences, workshops, or seminars. Consider pursuing certifications or specialized training in areas of interest, such as avionics systems, space systems, or aerodynamics.
- Build a Professional Network: Networking is crucial for career growth in any field. Attend industry events, connect with professionals through online platforms like LinkedIn, and join professional organizations. Building relationships with industry experts and fellow aerospace engineers can provide valuable insights, job opportunities, and mentorship.
Aerospace Engineer: Eligibility
To pursue a career as an aerospace engineer, here are the typical eligibility criteria:
- Educational Requirements: The first step is to complete your secondary education with a strong foundation in science and mathematics. To pursue a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a related field, you will generally need to meet the specific admission requirements of the university or college you plan to attend. These requirements often include a high school diploma or equivalent, satisfactory grades in science and mathematics courses, and sometimes English proficiency tests for non-native English speakers.
- Bachelor’s Degree: Obtain a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a closely related discipline. Most aerospace engineering positions require at least a bachelor’s degree. The program should be accredited by a recognized accrediting body to ensure quality education and eligibility for professional licensure if desired. The duration of a bachelor’s degree program is typically four years.
- Advanced Degrees (Optional): While not always mandatory, pursuing a master’s or doctoral degree in aerospace engineering can be beneficial, especially for those interested in research, advanced development, or academic careers. Advanced degrees provide a deeper understanding of specialized topics and can open up more advanced job opportunities. The decision to pursue further education depends on individual career goals and preferences.
- Relevant Skills and Knowledge: As an aspiring aerospace engineer, it’s essential to develop certain skills and knowledge areas. These include proficiency in mathematics, physics, and computer science, as these form the foundation for aerospace engineering principles. Additionally, problem-solving, critical thinking, analytical skills, and attention to detail are important qualities for success in this field.
- Internships and Practical Experience: Seek opportunities to gain practical experience through internships, co-op programs, or research projects during your undergraduate studies. This hands-on experience helps you apply theoretical knowledge, develop technical skills, and gain industry exposure. It also enhances your resume and increases your chances of securing job offers upon graduation.
- Professional Licensure (Optional): While not always required, obtaining a professional engineering license (such as a Professional Engineer or PE license) can be advantageous for career advancement and certain specialized positions. Licensing requirements vary by country or state, but typically involve completing an accredited engineering program, gaining relevant work experience, and passing a licensure exam.
Benefits of Becoming Aerospace Engineer

Becoming an aerospace engineer offers several benefits, both personally and professionally. Here are some key advantages of pursuing a career in aerospace engineering:
- Contribution to Innovation: Aerospace engineers are at the forefront of technological advancements and innovation in the aerospace industry. By working on cutting-edge projects, you have the opportunity to contribute to the development of new aircraft, spacecraft, and aerospace systems that push the boundaries of human exploration and transportation.
- Exciting and Challenging Work: Aerospace engineering offers a dynamic and challenging work environment. Designing, developing, and maintaining aircraft and spacecraft involves complex engineering problems that require creativity, problem-solving skills, and attention to detail. The diversity of projects and tasks keeps the work interesting and stimulating.
- Global Opportunities: Aerospace engineering is a global field, providing opportunities to work with international teams and collaborate on projects worldwide. This global perspective can broaden your horizons, expose you to different cultures and work environments, and facilitate networking and career growth on a global scale.
- Varied Career Paths: Aerospace engineering offers a wide range of career paths and specializations. You can choose to focus on areas such as aerodynamics, propulsion systems, avionics, materials, or space systems, depending on your interests and skills. This versatility allows you to explore different aspects of aerospace engineering and pursue your passion within the field.
- Competitive Salary and Benefits: Aerospace engineering is a specialized field that typically offers competitive salaries and benefits. The demand for qualified aerospace engineers remains high, particularly in industries such as aerospace manufacturing, defense, and space exploration. As you gain experience and expertise, you can expect to see increasing opportunities for career advancement and financial rewards.
- Impact on Society and the Future: Aerospace engineers play a significant role in shaping the future of air and space travel. By contributing to the design of safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly aircraft and spacecraft, you can have a positive impact on transportation, communication, scientific exploration, and even climate change mitigation efforts. The work you do as an aerospace engineer can contribute to a sustainable and technologically advanced society.
- Professional Fulfillment: For those passionate about aviation, space, and engineering, working as an aerospace engineer can provide a deep sense of fulfillment. Being part of a team that turns visionary ideas into reality, witnessing the successful deployment of aerospace systems, and knowing that your work contributes to the advancement of human knowledge and capabilities can be highly rewarding.
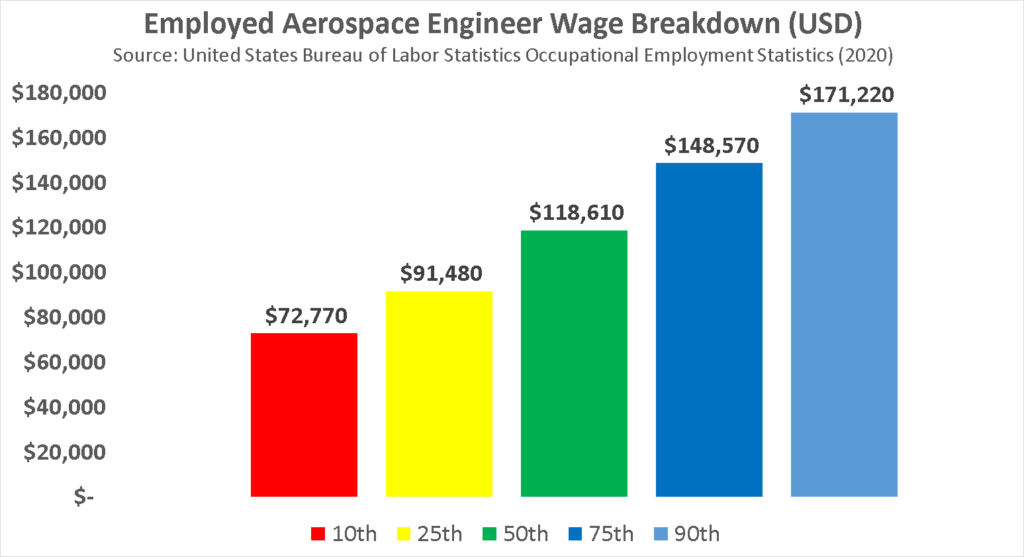
Jobs and Salary of Aerospace Engineer

| Job Position | Salary Range (INR) |
| Aerospace Engineer | 6,00,000 – 15,00,000 |
| Avionics Engineer | 5,50,000 – 14,00,000 |
| Systems Engineer | 5,00,000 – 12,00,000 |
| Aerodynamics Engineer | 5,50,000 – 13,00,000 |
| Propulsion Engineer | 5,50,000 – 14,00,000 |
| Structural Engineer | 5,00,000 – 12,00,000 |
| Flight Test Engineer | 6,00,000 – 15,00,000 |
| Spacecraft Engineer | 6,50,000 – 16,00,000 |
Aerospace Engineer: FAQs
What is the difference between aerospace engineering and aeronautical engineering?
Aerospace engineering encompasses both aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Aeronautical engineering focuses on the design and development of aircraft that operate within the Earth’s atmosphere, while astronautical engineering deals with the design and development of spacecraft and vehicles for space exploration.
What skills are important for aerospace engineers?
Important skills for aerospace engineers include strong mathematical and analytical abilities, proficiency in physics, computer programming skills, problem-solving skills, attention to detail, teamwork and communication skills, and the ability to think critically and creatively.
What industries hire aerospace engineers?
Aerospace engineers can find employment in various industries, including aerospace manufacturing companies, defense and military organizations, research and development institutions, government space agencies, aviation companies, and consulting firms specializing in aerospace engineering.
What are some common job roles for aerospace engineers?
Common job roles for aerospace engineers include aircraft design engineer, systems engineer, avionics engineer, propulsion engineer, structural engineer, flight test engineer, aerospace researcher, aerodynamics engineer, spacecraft engineer, and manufacturing engineer.
What are the educational requirements to become an aerospace engineer?
Most aerospace engineering positions require a bachelor’s degree in aerospace engineering or a related field. Some positions, especially in research or advanced development, may require a master’s or doctoral degree. It’s important to complete your education at an accredited institution to ensure the quality of your degree.
What are the future prospects for aerospace engineers?
The future prospects for aerospace engineers are promising. With increasing advancements in aviation technology, space exploration, and unmanned aerial systems, there is a growing demand for aerospace engineers. Additionally, aerospace engineers may contribute to emerging fields such as supersonic and hypersonic travel, electric propulsion, and autonomous flight.
Are there any licensure or certification requirements for aerospace engineers?
Licensure requirements for aerospace engineers vary by country and region. In some cases, professional licensure or certification may be required to work on certain projects or assume specific responsibilities. Examples include obtaining a Professional Engineer (PE) license or certifications in specialized areas such as avionics systems or aerospace structures.
